Heart attack kills, while brain attack cripples
A stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures and bleeds, or when there’s a blockage in the blood supply to the brain. The rupture or blockage prevents blood and oxygen from reaching the brain’s tissues.
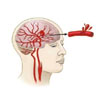
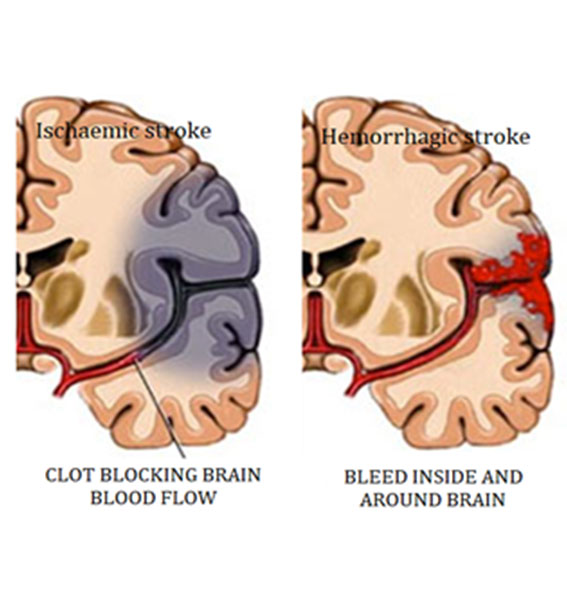
Hemorrhagic stroke
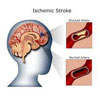
Ischemic stroke
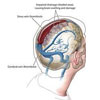
Venous Stroke
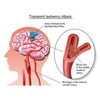
Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
The sooner a person having a stroke gets care (initial 6 hours is golden period), the better their outcome is likely to be. For this reason, it’s helpful to know the signs of a stroke so you can act quickly, which are paralysis, numbness or weakness in the arm, face, and leg, especially on one side of the body, trouble speaking or understanding others, slurred speech, confusion, disorientation, or lack of responsiveness, sudden behavioral changes, especially increased agitation, vision problems, such as trouble seeing in one or both eyes with vision blackened or blurred, or double vision, trouble walking, loss of balance or coordination, dizziness, severe, sudden headache with an unknown cause, seizures, nausea or vomiting or decreased alertness/ sensorium.
A stroke requires immediate medical attention. If you think you or someone else is having a stroke, call 911 or local emergency services right away. Usual complications are seizures, loss of bladder and bowel control, cognitive impairment, including dementia, reduced mobility, range of motion, or ability to control certain muscle movements, depression, mood or emotional changes, shoulder pain, bed sores, sensory or sensation changes Prompt treatment is key to preventing the following outcomes:brain damage, long-term disability, death.
Mostly require blood tests, blood sugar levels, whether you have an infection, platelet counts, cholesterol levels, MRI and CT scan, EKG, Cerebral angiogram, Carotid ultrasound, Echocardiogram apart from investigations focused on co-morbidities. Treatment for stroke depends on the type of stroke: Ischemic stroke and TIA need clot-breaking drugs (tPA), or Alteplase IV r-tPA, is considered the gold standard, mechanical thrombectomy, stents, surgery in hemorrhagic stroke., coiling, clamping. Medication for blood pressure, direct-acting oral anticoagulants, antiplatelet drugs, statins.