What are epileptic fits?
Epilepsy is a central nervous system (neurological) disorder in which brain activity becomes abnormal, causing seizures or periods of unusual behavior, sensations and sometimes loss of awareness. Anyone can develop epilepsy. Epilepsy affects both males and females of all races, ethnic backgrounds and ages. Around 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, making it one of the most common neurological diseases. Nearly 80% of people with epilepsy live in low- and middle-income countries. It is estimated that up to 70% of people living with epilepsy could live seizure- free if properly diagnosed and treated.

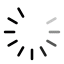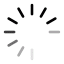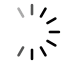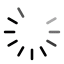
What lead to epilepsy?
It is due to diseased brain cells which episodically fires abnormal electrical signals at a higher current
more like a pacemaker.
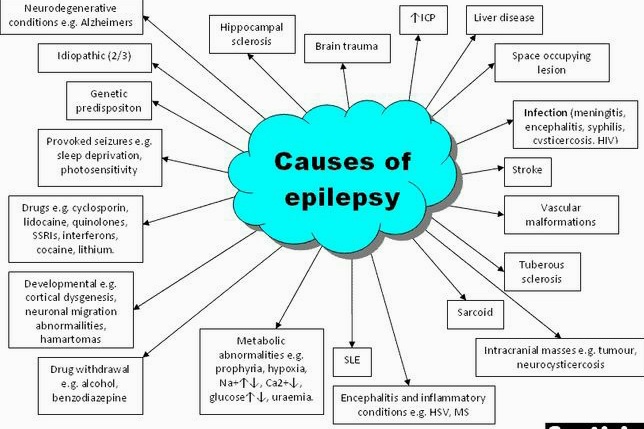
What are causes of epileptic fits?
Epilepsy is not contagious. Although many underlying disease mechanisms can lead to epilepsy, the cause of the disease is still unknown with certainty, in about 50% of cases globally. The causes of epilepsy are: structural, genetic, infectious, metabolic, immune and unknown. The last idiopathic seizures now have been proved due to genetic abnormalities: Known causes are brain damage from prenatal or perinatal causes (e.g., a loss of oxygen or trauma during birth, low birth weight); congenital abnormalities or genetic conditions with associated brain malformations; a severe head injury; a stroke that restricts the amount of oxygen to the brain; a brain infection such as meningitis, encephalitis or neurocysticercosis, certain genetic syndromes; and brain tumors.
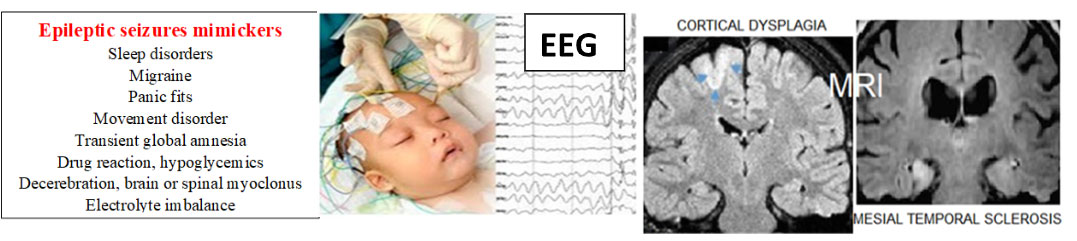
Epileptic disorders mimickers?
Diagnosis and treatment
Epileptic disorder diagnosis is made on the basis of GOOD HISTORY supported by neurological examination and investigations like EEG, MRI and blood tests, genetic counselling. It is a chronic treatable disease, cured in about 70 percent cases within 3-4 years drug treatment. Normal EEG and MRI does not excluded seizures. Mostly need 1-2 anti- epileptic drugs, addressing other comorbid conditions.
The EEG is done on an analog machine in a wakeful state, wherein patient need to be calm and relaxed, without any type of movements. In infants and children, the working of the neurons is evaluated by this testing after sedating them with drugs. It is always better to have a hair shampoo bath prior to this examination, after the test hair bah facilities are available in the center. Mostly with good co-operation of the patient these observations are completed within 40 minutes and reporting is given within half hour. In nerve conduction velocities or studies, speed and proper conduction of sensory, motor sensations are evaluated in the nerves, muscles, nerve roots in the spinal cord.
Electroencephalogram -EEG, Digital cognitive psychometric evaluation- CNSVS, VEP, BERA are tests conducted for evaluation of the function of the central nervous system and special senses (GYAN INDRIA) while the NCV, EMG, SSR testing is linked with peripheral nervous system; and are performed in nerve- muscle and spinal cord diseases (KARAM INDRIA).